- About
- Mission Statement
Education. Evidence. Regrowth.
- Education.
Prioritize knowledge. Make better choices.
- Evidence.
Sort good studies from the bad.
- Regrowth.
Get bigger hair gains.
Team MembersPhD's, resarchers, & consumer advocates.
- Rob English
Founder, researcher, & consumer advocate
- Research Team
Our team of PhD’s, researchers, & more
Editorial PolicyDiscover how we conduct our research.
ContactHave questions? Contact us.
Before-Afters- Transformation Photos
Our library of before-after photos.
- — Jenna, 31, U.S.A.
I have attached my before and afters of my progress since joining this group...
- — Tom, 30, U.K.
I’m convinced I’ve recovered to probably the hairline I had 3 years ago. Super stoked…
- — Rabih, 30’s, U.S.A.
My friends actually told me, “Your hairline improved. Your hair looks thicker...
- — RDB, 35, New York, U.S.A.
I also feel my hair has a different texture to it now…
- — Aayush, 20’s, Boston, MA
Firstly thank you for your work in this field. I am immensely grateful that...
- — Ben M., U.S.A
I just wanted to thank you for all your research, for introducing me to this method...
- — Raul, 50, Spain
To be honest I am having fun with all this and I still don’t know how much...
- — Lisa, 52, U.S.
I see a massive amount of regrowth that is all less than about 8 cm long...
Client Testimonials150+ member experiences.
Scroll Down
Popular Treatments- Treatments
Popular treatments. But do they work?
- Finasteride
- Oral
- Topical
- Dutasteride
- Oral
- Topical
- Mesotherapy
- Minoxidil
- Oral
- Topical
- Ketoconazole
- Shampoo
- Topical
- Low-Level Laser Therapy
- Therapy
- Microneedling
- Therapy
- Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy (PRP)
- Therapy
- Scalp Massages
- Therapy
More
IngredientsTop-selling ingredients, quantified.
- Saw Palmetto
- Redensyl
- Melatonin
- Caffeine
- Biotin
- Rosemary Oil
- Lilac Stem Cells
- Hydrolyzed Wheat Protein
- Sodium Lauryl Sulfate
More
ProductsThe truth about hair loss "best sellers".
- Minoxidil Tablets
Xyon Health
- Finasteride
Strut Health
- Hair Growth Supplements
Happy Head
- REVITA Tablets for Hair Growth Support
DS Laboratories
- FoliGROWTH Ultimate Hair Neutraceutical
Advanced Trichology
- Enhance Hair Density Serum
Fully Vital
- Topical Finasteride and Minoxidil
Xyon Health
- HairOmega Foaming Hair Growth Serum
DrFormulas
- Bio-Cleansing Shampoo
Revivogen MD
more
Key MetricsStandardized rubrics to evaluate all treatments.
- Evidence Quality
Is this treatment well studied?
- Regrowth Potential
How much regrowth can you expect?
- Long-Term Viability
Is this treatment safe & sustainable?
Free Research- Free Resources
Apps, tools, guides, freebies, & more.
- Free CalculatorTopical Finasteride Calculator
- Free Interactive GuideInteractive Guide: What Causes Hair Loss?
- Free ResourceFree Guide: Standardized Scalp Massages
- Free Course7-Day Hair Loss Email Course
- Free DatabaseIngredients Database
- Free Interactive GuideInteractive Guide: Hair Loss Disorders
- Free DatabaseTreatment Guides
- Free Lab TestsProduct Lab Tests: Purity & Potency
- Free Video & Write-upEvidence Quality Masterclass
- Free Interactive GuideDermatology Appointment Guide
More
Articles100+ free articles.
-
OS-01 Hair Review: Does It Live Up to the Hype?
-
Stretching The Truth: 3 Misrepresented Claims From Hair Loss Studies
-
Minoxidil Shedding – What to Expect & When it Stops
-
Does Minoxidil Cause Skin Aging?
-
Thermus Thermophilus Extract Does Not Increase Hair Density By 96.88%, Despite Dermatology Times’ Claims.
-
Does Retinoic Acid (Tretinoin) Improve Hair Growth From Minoxidil?
-
Topical Cetirizine: An Anti-Histamine That Regrows Hair? (New Evidence)
-
Scalp Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Effects on Hair Loss
PublicationsOur team’s peer-reviewed studies.
- Microneedling and Its Use in Hair Loss Disorders: A Systematic Review
- Use of Botulinum Toxin for Androgenic Alopecia: A Systematic Review
- Conflicting Reports Regarding the Histopathological Features of Androgenic Alopecia
- Self-Assessments of Standardized Scalp Massages for Androgenic Alopecia: Survey Results
- A Hypothetical Pathogenesis Model For Androgenic Alopecia:Clarifying The Dihydrotestosterone Paradox And Rate-Limiting Recovery Factors
Menu- AboutAbout
- Mission Statement
Education. Evidence. Regrowth.
- Team Members
PhD's, resarchers, & consumer advocates.
- Editorial Policy
Discover how we conduct our research.
- Contact
Have questions? Contact us.
- Before-Afters
Before-Afters- Transformation Photos
Our library of before-after photos.
- Client Testimonials
Read the experiences of members
Before-Afters/ Client Testimonials- Popular Treatments
-
ArticlesWhich Finasteride Is Best? A Look at Formulations
First Published Jan 20 2023Last Updated Oct 29 2024PharmaceuticalResearched & Written By:Perfect Hair Health TeamReviewed By:Rob English, Medical EditorWant help with your hair regrowth journey?
Get personalized support, product recommendations, video calls, and more from our researchers, trichologists, and PhD's dedicated to getting you the best possible outcomes.
Learn MoreArticle Summary
Finasteride is available in oral and topical formulations. Some hair loss sufferers opt for topicals, which have been touted as safe and effective by doctors and patients alike. Oral finasteride has stood the test of time and remains the gold standard for the treatment of male pattern hair loss. Which formulation is best for hair loss sufferers? The answer depends on an individual’s preferences for side effect mitigation, as well as their patterning of hair loss (i.e., localized versus diffuse). This post gives an overview of each formulation and offers insight into what is prescribed and why. It also explains how – contrary to popular belief – topical finasteride can still go systemic.
Full Article
What is Finasteride, and Which Finasteride is Best?
Finasteride is a drug approved by the FDA to treat benign prostate hyperplasia and androgenic alopecia. It is prescribed as a 1 mg daily tablet for men with androgenic alopecia. It is also prescribed in higher dosages for women suffering from female pattern hair loss. This ranges from 1.0-5.0 mg daily.
Finasteride is available in different formulations. The best option is determined on a patient-by-patient basis.
What Formulations of Finasteride are Available?
There are two main finasteride formulations: oral and topical. Doctors typically prescribe oral finasteride, as it’s a time-tested formulation with a high success rate. Many telehealth providers have sprouted up in recent years, offering topical and oral versions of the drug. Topical finasteride has become increasingly popular as more studies confirm its efficacy and relative safety versus oral finasteride.
As concluded in one study:
Topical finasteride significantly improves hair count compared to placebo and is well tolerated. Its effect is similar to that of oral finasteride, but with markedly lower systemic exposure and less impact on serum DHT concentrations. [1]https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34634163/
Clinical studies have shown that oral and topical formulations improve hair parameters equivalently in target area hair counts.[2]https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9297965/ As such, many people looking to minimize their risk of side effects from finasteride often prefer the topical formulation, and they rationalize that decision by arguing that topical finasteride (1) is just as effective as oral finasteride, and (2) remains localized to the scalp, so it must not have any systemic effects elsewhere in the body.
In reality, both of these arguments are wrong.
- While studies do show that topical finasteride is equivalent to oral finasteride in “target area hair counts”, hair count changes outside of these target zones have not yet been measured. Therefore, it is possible that topical finasteride may not protect against hair loss wherever it isn’t applied, whereas the oral formulation tends to provide global protection across the entire scalp. In fact, if topical finasteride does offer hair loss protection in non-applied scalp regions, the most likely reason is that the drug went systemic (i.e., entered into the bloodstream), traveled throughout the body, and redistributed to those non-applied areas. In that regard…
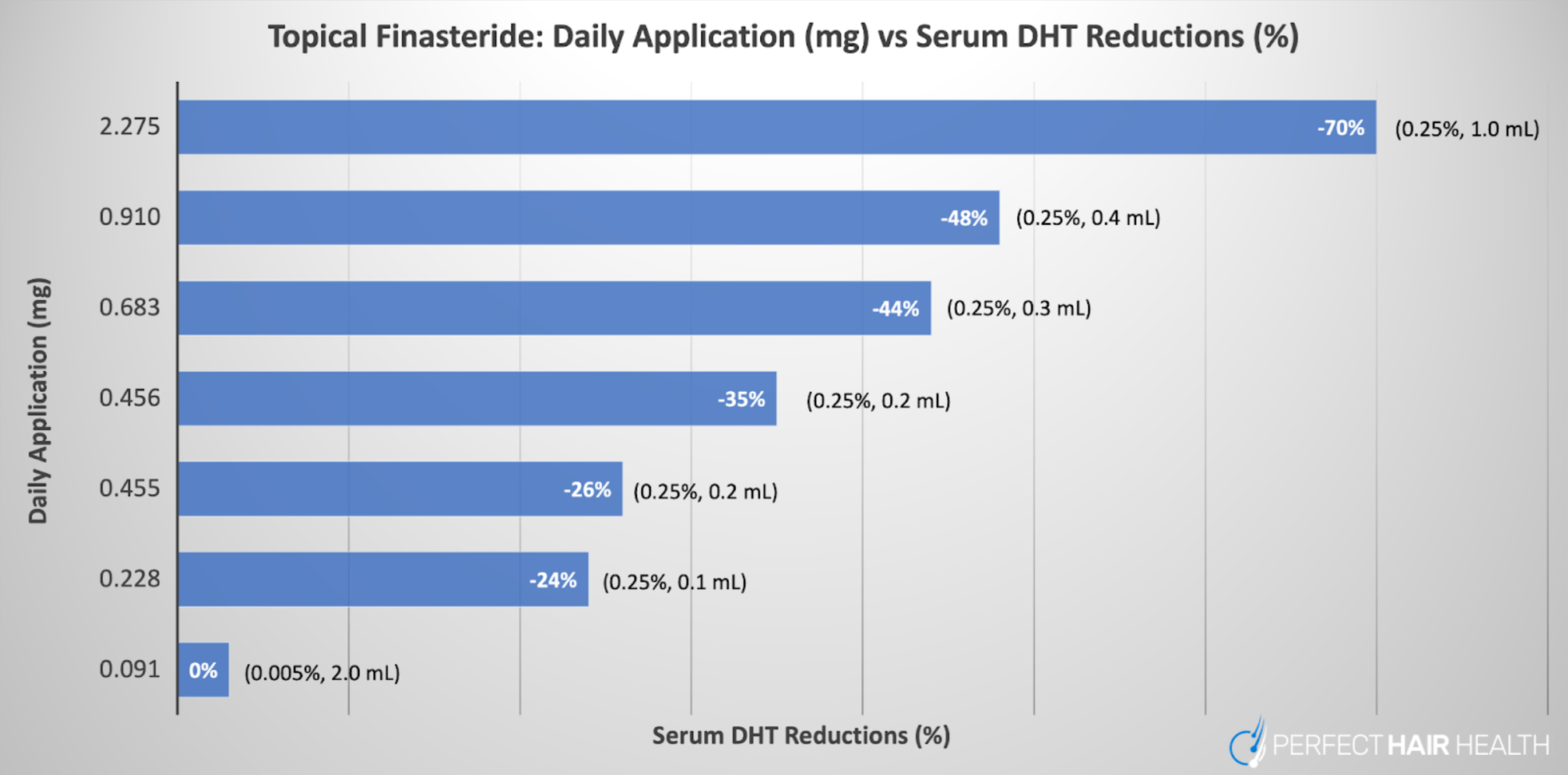
- Topical finasteride can go systemic, depending on the dose. Several studies show that topical finasteride also lowers blood levels of DHT, particularly for daily doses totaling greater than 0.1 mg of finasteride exposure. While the amount of drug in circulation is still far less than that of oral finasteride, people trying topical finasteride should know this, and titrate their topical formulations accordingly. Just see this chart:
A graph representing the daily dose exposure of topical finasteride (y-axis) versus the amount of serum DHT reductions in participants (x-axis). Across all studies referenced in the graph, topical finasteride led to hair parameter improvements.
Finasteride 1mg Oral Tablets
As mentioned, finasteride is typically prescribed as a once-daily 1mg tablet. At 1mg daily, finasteride is sometimes branded as Propecia®. Using more than 1mg per day isn’t likely to improve results.[3]https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10495375/
However, it may increase the risk of side effects. Nearly all clinical studies use 1mg, as it’s the gold standard for treating male pattern baldness. 5 mg finasteride is typically used to treat men diagnosed with benign prostatic hyperplasia (under the label Proscar®).
Oral Propecia® (i.e., 1mg daily of finasteride) is prescribed under its brand name and as a generic formulation through many telehealth companies. Generic versions of the drug typically deliver similar results, and often at a fraction of the cost.
Finasteride Topical Formulations
Finasteride topicals include gels, liquid solutions, and liquid sprays. Foams are available as well.
A previous post centered on the best topical finasteride dosage determined that finasteride has a highly-sensitive and dose-dependent response curve.
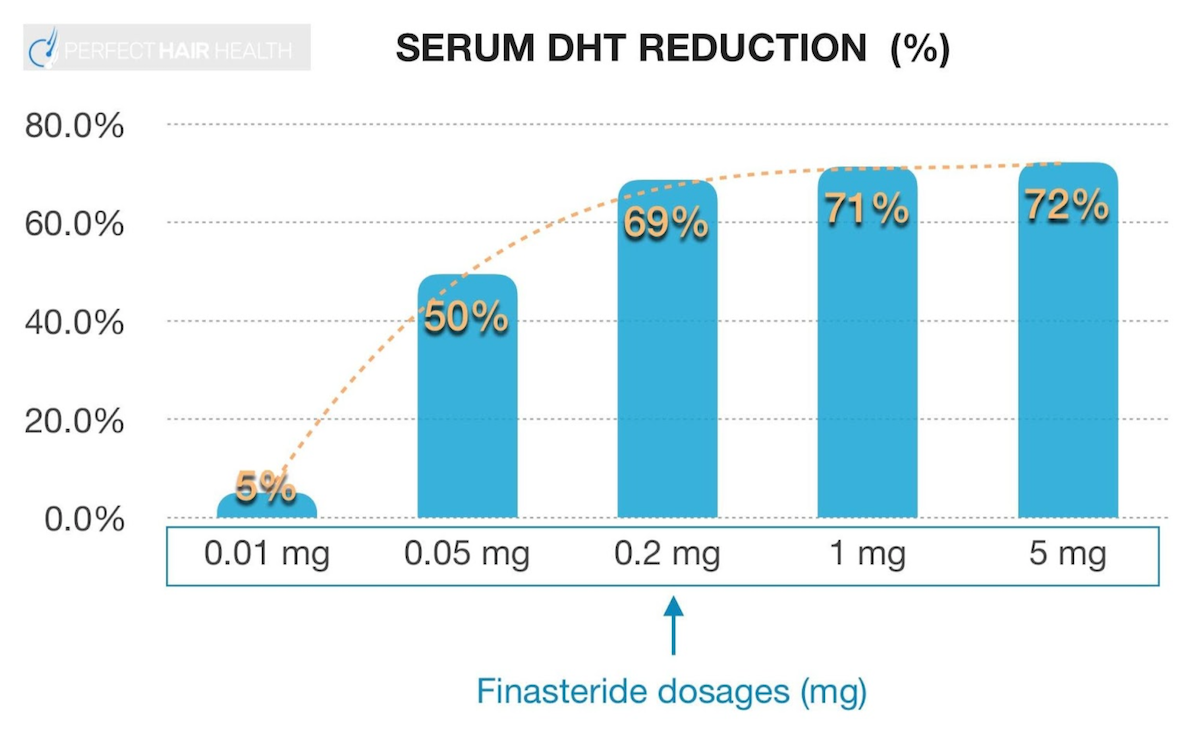
In other words, 0.01 mg of finasteride barely reduces any DHT, while 0.2 mg reduces almost as much DHT as 5 mg, a much larger dose.[4]https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jdv.17738 1% topical formulations essentially guarantee systemic absorption.
Those aiming to avoid the side effects may want to consider a formula with lower percentages of the active drug.
Which Finasteride Is Best for Hair Loss?
It depends on two factors: (1) the presence of side effects, and (2) whether a patient has diffuse thinning or localized hair loss.
Side effects
When weighing the pros and cons of finasteride formulas, doctors often have patients start with oral finasteride. This is because oral finasteride has the strongest clinical evidence for treating male pattern hair loss, and it provides some degree of protection across all balding-prone areas.
If side effects occur on oral finasteride at 1 mg daily, doctors may consider lowering the dose to 0.2 mg daily to see if this reduces side effects. If issues persist, other options can be explored – such as topical formulations.
Under these circumstances, users may introduce topical finasteride at a 1-2 mL daily of 0.025% to 0.3% finasteride. If side effects persist, it may be necessary to lower that dose all the way to 0.005% x 2 mL daily, and start tracking serum DHT levels to measure – as a proxy – how much finasteride is actually going systemic (as these levels vary greatly depending on the person and any adjuvant treatments that might be influencing topical absorption – i.e., retinoic acid, microneedling, etc.).
Hair loss patterning
If someone wants to use topical finasteride, they should recognize that topical formulations of the drug are most appropriate for people who have localized hair loss (i.e., hair loss only at the temples and/or crown), rather than people with diffuse thinning (i.e., hair loss throughout the entire scalp).
This is because diffuse thinners have a larger area of the scalp to cover with a topical. That requires a higher amount of mL per application daily of topical finasteride to cover all zones. When holding constance the percentage dilution of topical finasteride, the more mL applied daily, the higher likelihood some of that additional finasteride will leak into the bloodstream and cause systemic effects – thereby defeating the whole effort of the topical in the first place.
For these reasons, diffuser thinners need to take extra care to titrate down their topical finasteride doses, or perhaps consider oral formulations of finasteride to maximize their scalp coverage and thereby improve their odds of long-term success.
For those who don’t experience any sexual side effects, long-term use of oral finasteride may be advisable, given its success rate. And for those who experience adverse systemic effects of oral finasteride, or those wary about potential issues with the oral formulation, topical finasteride may be the better option.
Want help with your hair regrowth journey?
Get personalized support, product recommendations, video calls, and more from our researchers, trichologists, and PhD's dedicated to getting you the best possible outcomes.
Learn MorePerfect Hair Health Team
"... Can’t thank @Rob (PHH) and @sanderson17 enough for allowing me to understand a bit what was going on with me and why all these [things were] happening ... "
— RDB, 35, New York, U.S.A."... There is a lot improvement that I am seeing and my scalp feel alive nowadays... Thanks everyone. "
— Aayush, 20’s, Boston, MA"... I can say that my hair volume/thickness is about 30% more than it was when I first started."
— Douglas, 50’s, Montréal, CanadaWant help with your hair regrowth journey?
Get personalized support, product recommendations, video calls, and more from our researchers, trichologists, and PhD's dedicated to getting you the best possible outcomes.
Join Now - Mission Statement
 Scroll Down
Scroll Down